Mechanics of Structures
Mechanics of Materials and Structures
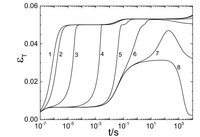
Precipitates in solids usually provoke a misfit-stress state due to a misfit – eigenstrain state. Relaxation of this stress state by creep is the relevant mechanism to reduce the often high level of the misfit-stress state. This process is also associated with growth/shrinking of precipitates due to the influence of the stress state on the diffusion process.
Mechanics of Materials and Structures
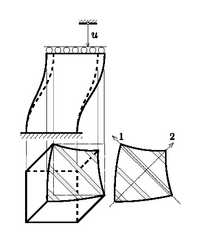
Elastoplastic buckling of layered micropillars and microstructures requires a correct interpretation of the experimental results, particularly due to geometric effects, which often are addressed to material properties (cooperation with TU-Vienna, MPI-Düsseldorf).
Mechanics of Materials and Structures
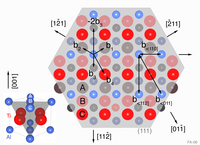
Modelling concepts for intermetallic titanium aluminides are presented in a review on former concepts, particularly concerning plasticity modified by twinning, together with a concept to understand formation of twins (related to displacive phase transformation (in cooperation with GKSS Geesthacht)).
Stress, deformation state and life time of structures, like storage tanks and vessels during earthquake excitation Partners: ESI Leoben, Kolednik Analysis Micromechanics of forming tools during thermomechanical treatment, development of defects and irreversible shape changes Partners: MC Leoben, R. Ebner et al. Stress and deformation state in biological structures, swelling and shrinking mechanisms during life time Partners: MPI Colloids & Interfaces, Potsdam/Golm, Fratzl et al. Dynamics of the railway wheel/rail or wheel/switch contact process. Deformation, stress and wear state in the wheel and the rail or switch Partners: MC Leoben, Daves; VA Schienen GmbH Leoben; VAE Zeltweg